to ESG governance
Since its inception, Reliance has been committed to sustainable growth, which has only been possible due to the underpinning governance. The Company recognises the role of robust governance mechanisms for long-term value creation. Efficient corporate governance has acted as a pillar of Reliance's sustained growth throughout the year.
Reliance's Corporate Governance practices are driven by the principles of transparency, accountability, and integrity. This is operationalised by relevant policies and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to ensure compliance and good governance for all stakeholders.
Board Governance
Reliance’s senior leadership comprises of a 14-member Board which is responsible for direction and oversight of Reliance. The Board of Directors come from diverse backgrounds with unique competencies and rich experience. The induction into the Board of Directors is instituted by the Board level Human Resources, Nomination and Remuneration Committee. This Committee oversees aspects which include formulation of the criteria for determining qualifications, positive attributes, and independence of a Director, and recommend to the Board a policy, relating to the remuneration of the Directors, Key Managerial Personnel, and other employees. The Committee has also developed a set of criteria for evaluating the performance of the Board of Directors, including that of Independent Directors. Attendance, familiarity with the business, and engagement are some of the key parameters defined for evaluating the Board's performance. The Board of Directors, through its Committees, oversee the ESG initiatives and performance.
Board diversity in skill-set, nationality, experience, and perspective is important for effective leadership and governance. A diverse Board provides guidance and effective oversight over the Company's operations. It enhances responsiveness to stakeholder needs, collaboration across departments, and provides expertise leading to the continuous growth of the Company. Presently, the Board consists of two eminent women directors.
Regulatory Issues and Compliance
Regulatory compliance at Reliance has been of utmost importance, especially in an evolving regulatory scenario. Reliance’s Regulatory compliance risk is addressed by the Reliance Compliance Management System. It is a digitally enabled comprehensive compliance management framework that's integrated with business processes, risks and controls and updated on a regular basis.
Changes in regulations are also monitored on an ongoing basis by the Group Compliance Committee. The Directors get monthly or quarterly information on key statutory and regulatory developments, as well as key judicial rulings affecting interpretation of important laws.
More information is available on https://www.ril.com/ar2020-21/pdf/ Risk%20and%20Governance.pdf
ESG Governance
Reliance is on a continuous improvement journey to create long- term value for its stakeholders. The key decisions that are taken pertaining to ESG include indepth analysis through an Integrated Profit and Loss lens. Reliance has integrated ESG into its governance structure so that the Company can have a better oversight and strengthen management responsibility for business-related ESG challenges and opportunities.
The Corporate Social Responsibility & Governance (CSR&G) Committee oversees the implementation of sustainability activities. Business Responsibility Report (BRR) describing the initiatives taken by the Company from an environmental, social and governance perspective is reviewed and recommended to the Board by the CSR&G Committee. The progress on the Company’s CSR initiatives is periodically reviewed by the CSR&G Committee and the Company’s Board of Directors. RIL continuously enhances its existing systems and processes to capture the impact of its social/economic and developmental initiatives. The Risk Management Committee oversees the ESG related risks and risk mitigation measures. Further, the Health, Safety & Environment (HSE) Committee reviews the environment related policies and matters.
Detailed information on various Board Committees is available on https://www.ril.com/OurCompany/Leadership/ BoardCommittees.aspx and the Corporate Governance section of this report.
Policies and Codes
Policies and codes are the essential components that help operationalise governance frameworks. Reliance's policies and codes signify the Company's commitment to the highest business ethics and corporate values and are communicated transparently to all the relevant stakeholders. A detailed list of policies is available in the Corporate Governance Section of this report.
Code of Conduct
With strict adherence to its Code of Conduct Policy, RIL maintains its reputation and continues to earn the trust of its stakeholders. A robust Code of Conduct Policy ensures integrity, accountability, and transparency in the Company. RIL's code lays down the responsibilities and expectations for the Directors, Business Partners, Employees, Suppliers, and other stakeholders. To deal with ethical transgressions in the organisation, the Company has established the Vigil Mechanism, Whistle blower Policy, and Ethics & Compliance Task Force (ECTF).
More information is available at https://www.ril.com/DownloadFiles/ IRStatutory/Code-of-Conduct.pdf
Details of Reliance's governance policies and codes can be accessed on its website: https://www.ril.com/ investorrelations/downloads.aspx

Towards Clean and Alternative Energy:
Reliance Net Zero
Reliance's Goal
Reliance believes that although climate change is a global threat, but tackling it in a timely manner can offer an opportunity to create a healthier, happier, more secure and resilient future. Therefore, the global New Energy agenda has to transcend from dialogue to action and commitment through urgent on-ground implementation. Led by this vision, Reliance had announced a target to be Net Zero by 2035. To achieve this ambitious goal, Reliance announced to:
- Establish and enable 100 GW of solar energy by 2030
- Build Giga Factories to create and offer a fully-integrated, end-to- end renewable energy ecosystem
- Invest in value chain, partnerships and future technologies, including upstream and downstream industries
- Transform its business to Net Carbon Zero operations
Reliance's Commitment
As the world develops new technologies to combat the effects of climate change, Reliance has embraced the need of the hour and spearheaded its initiatives towards decarbonisation. The Company is transforming itself, embracing new- age technologies and establishing a comprehensive green energy ecosystem in India, ranging from solar modules and batteries to hydrogen fuel cells.
Reliance sees investments in renewables and alternative energy as an active way to ensure positive outcomes for future generations. With renewables and alternative energy dominating the future power generation mix, the Company is changing the way it operates.
As one of the biggest energy markets globally, India will play a key role in transforming the world's energy landscape. The country has already announced its National Hydrogen Mission, which aims to boost green hydrogen production. As a Company that is always focused on growing businesses of the future and making India a stronger economy, Reliance will lead by leveraging its strengths that include finance, talent, technology, and proven project execution capabilities. The Company aims to play a meaningful role in meeting the country's growing energy demand sustainably by making its New Energy business truly global.
Reliance's Strategy
As a part of Reliance’s long-term strategy on emission reduction, the Company is committed to reducing its overall operational GHG footprint – Scope 1 or direct emissions and Scope 2 or indirect emissions from energy purchase.
The O2C Net Zero plan is anchored on six key strategic initiatives, which are as follows:
Improving energy efficiency
Energy transition to clean and green renewable energy from fossil fuels
Repurposing of petcoke gasification streams to utilise syngas for producing chemicals and hydrogen
Producing syngas on a renewable basis through biomass gasification
Using Carbon Dioxide (CO2) as a recyclable resource and adopting Carbon Capture Utilisation and Sequestration (CCUS) pathways such as but not limited to synthetic fuels and chemicals, mineral carbonation in construction materials, algae cultivation for biofuels and food supplements, and other technology-led solutions
Generating carbon credits and using them to offset hard-to-abate emissions
The Company is already accelerating its progress through resource efficiency and energy conservation. As the business evolves towards its Net Zero target, digitalisation is one factor that enables the ecosystem. Reliance is using its global collaboration to help establish the feasibility and successful deployment of CCUS.
The Company's initiatives will contribute towards the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) to combat climate change, ensuring sustainable consumption and production patterns, and ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all.

Reliance's Approach
Reliance is on the path of transformation to move its legacy businesses to Net Zero operations and improve it further with the best Corporate Governance and sustainability systems.
The Company has already enlisted eight global technocrats, many of whom are advisers to governments worldwide, as part of a nine member New Energy Council. This Council will be vital in leading an accelerated transition and providing futuristic solutions to practical problems that may arise along the way.
Reliance's approach is to create a New Energy ecosystem, transition to clean energy and convert clean energy to Green Chemicals.
The Company has made substantial progress on photosynthetic biological pathways to convert CO2 emissions at Jamnagar into high-value proteins, nutraceuticals, advanced materials, and fuels. The Company is taking strong strides in its journey to develop the next-gen Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies. It is also evaluating options to convert novel catalytic and electrochemical transformations to use CO2 as a valuable feedstock.
Reliance has also embarked on making changes in the present business, using less carbon-intensive alternatives and changing the legacy business model. Promoting a net- zero strategy in energy production and consumption is a key focus area for the Company. Championing an aggressive energy transition, Reliance sees a significant opportunity in hydrogen and alternate energy as the key to developing its business of the future. While doing so, the Company is selecting meaningful technologies for building a portfolio that has the most efficient, smart and sustainable solutions.
Alignment with WEF-IBC Core Metrics
| Theme | Report Section | |
|---|---|---|
 Pillar-1 Governance |
Governing Purpose Quality of governing body Stakeholder Engagement Ethical behaviour Risk and opportunity oversight |
Corporate governance section Read More; Corporate governance section Read More Responding to the Material Issues Read More Corporate governance section Read More; Management Discussion and
Analysis Report Read More; |
 Pillar-2 Planet |
Climate Change |
Natural capital Read More; Progress 
|
 Pillar-3 People |
Dignity and Equality Health and well‑being Skills for the future |
Corporate governance section Read More; Human capital Read More Human capital Read More Human capital Read More 
|
 Pillar-4 Prosperity |
Employment and wealth generation Innovation of better |
Human capital Read More; Intellectual capital Read More  
|
Progress towards Task Force on Climate Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
In its quest to strengthen climate- related disclosures and the management and reporting of climate-related risks in response to the TCFD recommendations, the Company is further strengthening its endeavour to move towards Net Zero. In line with the TCFD risk methodology, it takes into cognisance climate-related risks that may hamper the Company's growth. It has instituted steps to hedge such identified risks using proper lines of control.
Governance
Governance is one of the most vital components of a company's climate risk framework. This pillar covers the Governance framework, roles, responsibilities, and decision- making procedures by which a company adheres to its climate- related commitments. Reliance has a robust Governance structure to identify and mitigate climate- related risks and opportunities. The Company's material issues that may impact climate change are assessed at regular intervals. The Governance structure followed at Reliance to oversee climate change risk mitigation includes:
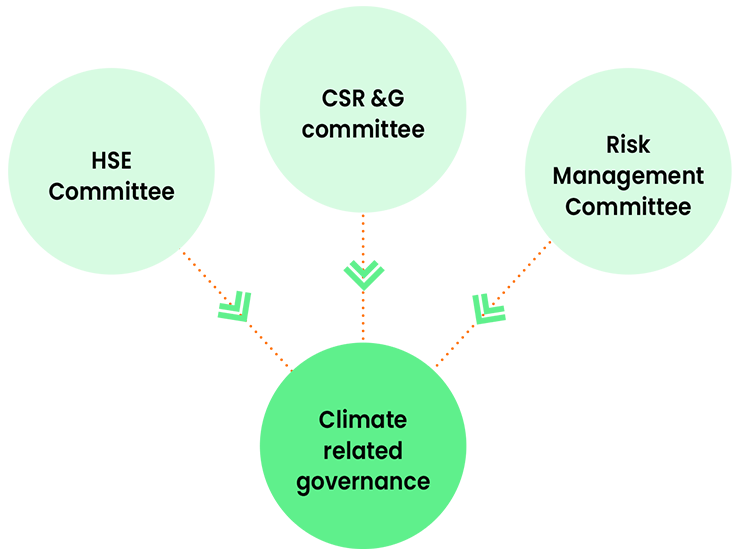
The HSE Committee has broad oversight on climate-related governance. The HSE Committee, CSR & Governance and the Risk Management Committee oversees Company's ESG initiatives.
Strategy
Reliance conducts a deep analysis of the climate-related nuances of all its businesses to formulate critical strategic advantages and competitive strengths of each segment. The structured materiality assessment process also helps determine issues vital to individual business units and Reliance. The Company has outlined its way to decarbonise in Reliance's Net Zero Strategy.
A detailed discussion on the Company's New Energy Business to achieve Net Zero by 2035 is provided in the MD&A section of this report.
Risk and opportunities
Climate-related risks pose threats that have financial implications for organisations, such as direct damage to assets and indirect impacts on the supply chain. Reliance identifies such risks at the Corporate and site levels through integrated work processes and group-wide risk management. It applies an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework using top-down and bottom-up approaches to anticipate any issues and mitigate their impacts in advance. Climate-related risk management initiatives are analysed through the lens of physical and transition risks. To facilitate continuous and real-time risk assessment, Reliance has implemented a 'Three Lines of Defense' model that encapsulates:
- First line of defense by Business/ Process managers through Self-verification
- Second line of defense by the Risk Management team through Functional Assurance
- Third line of defense by the Internal Audit and Management Assurance Function offering Independent Assurance
Reliance’s business operations face risks from natural calamities due to the vast spread of its operational locations. Natural calamities which are largely resultant of climate change are being manifested in terms of heat waves, erratic rainfall, cyclones, floods, and drought.
The Company has created Global Corporate Security (GCS). It is a dedicated and distinct function that focuses on adopting pre-emptive, de-risking strategies to safeguard and secure the Company from disasters, natural calamities, and any other disruptions or incidents as a part of business continuity management. GCS ensures that the people, assets, and operations of Reliance are secure.
To combat climate change, Reliance has embarked on an ambitious journey to transition to new, green, and clean energy. However, this transition to a lower carbon economy brings its own set of risks which include dynamic policy, legal, regulatory, technology and market developments and changes to facilitate this transition.
Reliance sees a significant opportunity in hydrogen and alternate energy. Details on the Company’s energy transition plan is provided in the Natural Capital section and the details on creating a green energy ecosystem is in the New Energy section.
Metrics and Targets
The disclosure on Metrics provides information on how the Company is progressing towards targeted climate-related indicators. These are the mechanisms for measuring and disclosing the progress in line with the commitments or ambitions set for managing and mitigating the impact of climate-related risks. Reliance consistently discloses its metrics, goals, and progress against them in its Annual Integrated Report.
Reliance's assured climate-related parameters and performance metrics can be found in the section on Natural Capital on read more of this report.
We Care: Maximising Shared Value
Reliance adopts a stakeholder centric approach when making business decisions. Understanding stakeholder expectations and aligning business objectives are critical to Reliance's growth. The Company regularly engages with its stakeholders to seek constructive feedback and systematically identify and resolve their concerns.
Reliance has developed robust processes to communicate and engage with various stakeholder groups and instituted necessary measures to meet their requirements and expectations appropriately. The Company strives for economic and ecological sustainability through these interactions and pre-empt and manage future uncertainties.
Reliance's Stakeholder engagement approach and inter-linkage with the Capitals:
| Stakeholder Group |  |
Employees | Investors | Customers | Suppliers | NGOs | Communities | Government and Regulatory Authorities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For Reliance, employees are at its core and one of its most valuable assets driving its consistent success. Reliance is committed to providing a progressive workplace focused on its employees' overall development and well-being. | Investors play a critical role in bolstering the Company's financial position and ensuring its operational success. Reliance is committed to creating value for its shareholders through implementing scalable business strategies. | Reliance places a great emphasis on ensuring that the requirements of its customers are understood and met. Reliance aspires to be the brand of choice for all its customers and remain relevant through its customer- centric approach. | Reliance fosters long- term relationships with its suppliers and ensures compliance with the Business Partner Code of Conduct policies. The Company believes that its suppliers enable the organisation to source responsibly and adhere to the highest standards. | Reliance works together with Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) to achieve holistic growth and broaden the scope of its objectives. | Reliance strives to provide value to local communities to maintain its social licence to operate. By contributing to the upliftment and growth of its surrounding communities, the Company aspires to prosper with them. | Government policies and regulations impact Reliance's operations and open up new avenues for the Company to pursue its goals. | ||
Functions |
 |
|
|
Business Teams:
|
|
|
|
|
Engagement Channels |
 |
Personal/group interactions, mailers, trainings, employee satisfaction survey, townhalls |
Meetings, conferences, investor calls, roadshows and correspondence |
Meetings, surveys, web portals |
Meetings and through Annual Reports or compliance filings |
Meetings and correspondence, participatory development activities, project planning and implementation meetings, capacity building and communities of practice |
Meetings, newsletters, surveys, fieldwork and trainings, digital services, virtual engagement |
Industry representations, filings, correspondence, meetings |
Frequency |
 |
Annually, Quarterly, monthly, need-based, real-time |
Annually, |
Annually, monthly, need-based, real-time |
Real-time, need-based |
Annually, ongoing partnerships |
Annually, ongoing partnerships |
Annually, ongoing partnerships |
Key Factors |
 |
Employee well-being, health and safety, performance reviews, career development conversations, training, and upskilling |
Financial performance, growth plans and strategies, shareholder returns and dividends |
Customer experience, product and service quality, Reliance's response to demands and expectations |
Terms and conditions, procedures, and payments |
Community development, Public infrastructure development, community health and well-being, enable communities to achieve their potential |
Community needs and expectations, financial and medical support, health, nutrition, and livelihood enhancing efforts, building capacities and training |
Compliance with regulatory requirements, collaboration in government-led sectoral plans and programmes |
Impact on Capitals |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Natural Capital
Natural Capital
 Human Capital
Human Capital
 Manufactured Capital
Manufactured Capital
 Intellectual Capital
Intellectual Capital
 Social and Relationship Capital
Social and Relationship Capital
 Financial Capital
Financial Capital


